1. Manufacturing and Engineering: Engineers, technicians, production managers.
Average Salary: $8,000 to $20,000 per year.
2. Tourism and Hospitality: Hotel managers, tour guides, restaurant staff.
Average Salary: $6,000 to $15,000 per year.
3. Textile and Garment Industry: Textile engineers, fashion designers, production managers.
Average Salary: $6,000 to $15,000 per year.
4. Real Estate and Construction: Architects, civil engineers, project managers.
Average Salary: $8,000 to $25,000 per year.
5. Agriculture and Farming: Farmers, agricultural scientists, agribusiness professionals.
Average Salary: Salaries vary widely, with many farmers being self-employed.
- Working Hours. The standard working week in Vietnam is 48 hours, typically spread over six days.
- Annual Leave. The standard is 12 to 20 days per year, depending on the number of years worked.
- Sick Leave. Employees are entitled to sick leave with full pay based on the duration of their illness.
- Maternity Leave. Female employees are entitled to maternity leave, and the duration varies depending on the number of children and other factors.
- Public Holidays. Vietnam observes several public holidays, and employees are generally entitled to take these days off with full pay. Some major public holidays include Tet (Lunar New Year), Independence Day, and National Day.
- Minimum Wage: The minimum wage varied by region, with higher rates in urban areas. For example, in Region I (including Ho Chi Minh City and Hanoi), the minimum wage was around VND 4,420,000 per month.
- Average Wages: Average wages in Vietnam can vary widely depending on the industry, job sector, and the level of experience or skill. In major cities and industrial zones, employees in sectors like information technology, finance, and manufacturing tend to receive higher salaries compared to other fields.
1. Startup Culture:
Vietnam has embraced a startup culture, with a surge in the number of young entrepreneurs establishing innovative businesses.
2. Government Initiatives:
The Vietnamese government has implemented various initiatives to encourage entrepreneurship and innovation. Support programs include funding schemes, tax incentives, and mentorship opportunities for startups.
3. Emerging Industries:
Information technology, e-commerce, fintech, and renewable energy are among the rapidly growing sectors for entrepreneurs.
4. Startup Hubs:
Ho Chi Minh City and Hanoi are prominent startup hubs, hosting co-working spaces, incubators, and accelerators.
5. Challenges:
Despite the positive environment, entrepreneurs may face challenges such as bureaucratic hurdles and the need for clearer regulatory frameworks.
1. Ho Chi Minh City (Saigon): a major business hub. It hosts a diverse range of industries, including finance, technology, manufacturing, and trading.
2. Hanoi: a political and economic center with a rich history. Hanoi is particularly significant for industries such as finance, technology, and tourism.
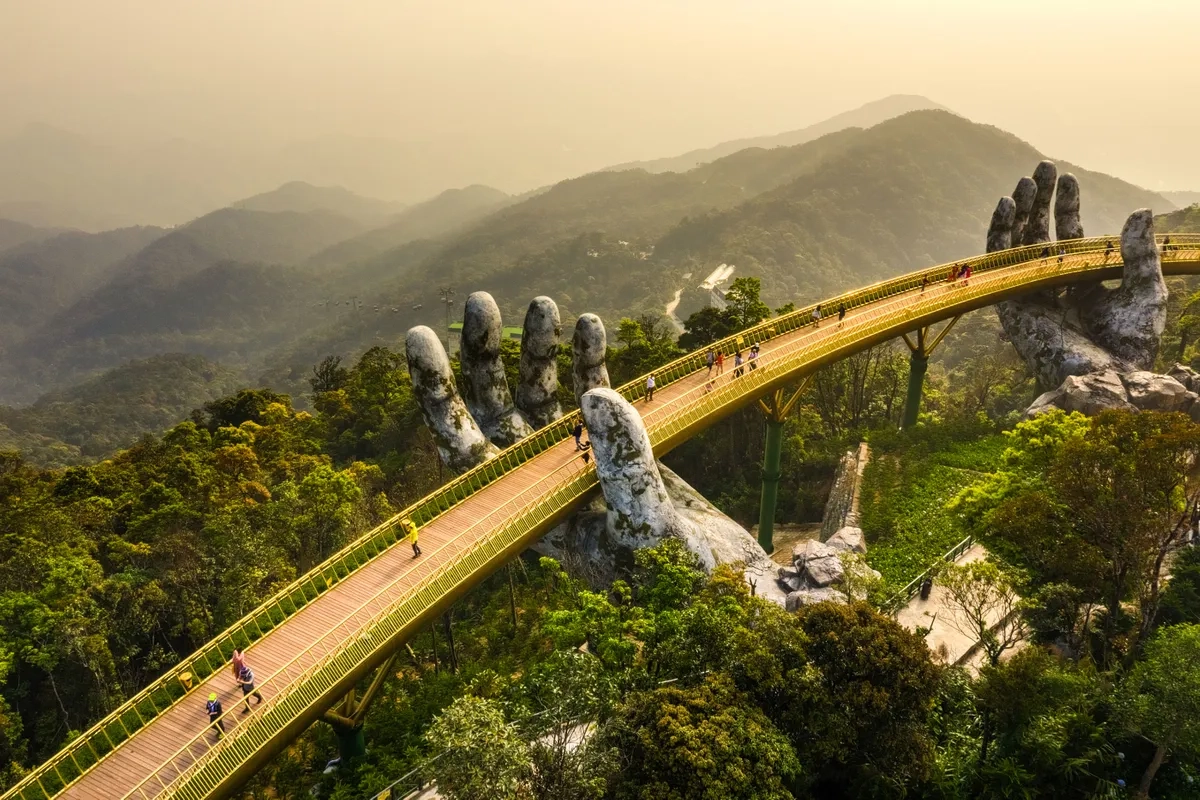
3. Da Nang: a coastal city with a rapidly developing economy. Its strategic location makes it a key player in trade, logistics, and tourism.
4. Hai Phong: a major port city and industrial center in northern Vietnam. Its strategic location near Hanoi and proximity to key transportation routes make it a hub for manufacturing and logistics.
5. Can Tho: a vital economic center for the southern region. It is known for its agricultural and aquaculture industries.